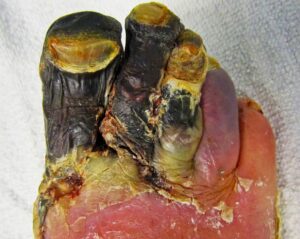
Hello everyone!!! Let us first understand what is gangrene and it’s role in diabetes. Gangrene is a condition whereby there is poor blood circulation to the tissues leading to the death of the cell tissue and necrosis due to lack of blood supply. When the blood glucose levels are increased in the blood, there is poor circulation of blood to the tissues which leads to Gangrene. There are two types of Gangrene namely: Dry and wet gangrene. Gangrene usually occurs in extremities hands , legs, toes, fingers.
Common symptoms of Gangrene are:
- Degenerative changes in the tissue
- The affected area becomes brown and then turns black.
- Pain with numbness of the affected region.
About half of the Indian population is suffering from diabetes and from that one forth of the population suffer from gangrene.
Diabetic foot:
Diabetic foot is a complication of prolonged uncontrolled Diabetes. According to Wagner’s classification, Diabetic foot is graded into five grades:
- 0- when the skin over the foot is intact
- I -superficial ulcer
- II -deep ulcer occurs
- III -osteomyelitis of bone /deep abcess/pus formation
- IV – front of the foot gangrene
- V -heels and back of the foot affected gangrene
Factors that lead to Diabetes Gangrene (causes):
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Obesity
- Varicose veins
- Autoimmune diseases
- Frostbite
- Trauma/injury
Types of Gangrene:
Dry gangrene:
In this type of gangrene, the blood sugar level is high which leads to loss of blood supply to the peripheral tissue. The skin becomes brown first and later on black. There is a lot of pain and numbness of the affected area like foot or hand.
Wet gangrene:
This type of gangrene usually occurs in both type 1 and type 2 Diabetes. This results in blister, pain and swelling of the affected area due to infection. Th affected region becomes black and there is accumulation of pus inside which later oozes out. Along with that, there is itching and pain of that area. Diabetic foot is also called as gangrene. This also results in neuropathy of the affected area resulting in numbness of the region. Wet gangrene is usually bacterial infectious. The affected region is infected by streptococcus or Escheria bacteria or Clostridius perfrigenous bacteria.
Gas gangrene:
Gas gangrene is a bacterial infection that produces gas within tissues caused by clostridium perfringens and other toxic bacterias. It is accompanied with pain, swelling and gas in the tissue and lot of inflammation.
Necrotising fasciitis (NF) is a deep tissue infection caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus or Streptococcus leading to similar symptoms of wet gangrene.
Noma gangrene:
Here the gangrene refers to the face due to increased blood sugar levels.
Fournier’s gangrene:
This refers to gangrene of the genitals causing pain, swelling and fever. Wet gangrene when worsened can also lead to fever and sepsis. It can also affect the fertility of the patient. Appropriate control measures must be taken for controlling both diabetes and gangeene.
Meleney’s gangrene:
This type is very rare and usually causes painful lesions on your skin within 2 weeks after surgery or minor trauma.
Internal gangrene:
This usually occurs in the internal organs especially appendix and colon. The patient has a lot of pain in right hypochondriac region with vomiting coinciding syptoms of appendicitis. But here there is another indication of increase prolonged diabetes.
Treatment and Management of diabetes and Gangrene:
- Manage your disease conditions. If you have diabetes, please keep a regular check of blood sugar levels, any kind of slow healing injury andaskin disease etc.
- Wounds. Take medical immediately if you see signs of infection.
- Avoid smoking. As smoking damages the blood vessels.
- Mantain your weight as per BMI. Extra weight can exert pressure on your arteries thus blocking blood flow.
- Keep yourself warm. Frostbite also blocks blood flow and the skin becomes pale, numb and can lead to gangrene.
Diagnosis:
Blood test: Get the blood tests done, glucose levels tested both fasting and post pariandal levels. One needs to monitor the glucose levels in the blood every month in case of gangrene. Also blood culture can help conclude the bacteria like steptococus, clostradial infections.
MRI/CT scan of vital organs necessary for ruling out internal Gangrene. Also it determines the extent of spread internally in skin, fascia, tissue etc.
X-ray of foot or hand suggestive of any injury leading to gangrene. Appropriate measures must be taken as per symptomatology.
Treatment of Gangrene and diabetes.
Treatment of gangrene involves removing dead tissue, treating and stopping the spread of infection. Treating the causative condition that caused the gangrene leads to speady recovery.
Treatment usually depends on the type of gangrene and may include:
Surgery. This is also called debridement. Dead tissue is removed to control the sprwsp of infection. This might need to remove an affected limb, finger or to also known as amputation.
Oxygenation of the affected region:
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can treat gangrene or ulcers related to diabetes or peripheral artery disease. Patient needs to spend time in a special chamber filled with oxygen at a higher pressure than oxygen found in the outside air. This high level of oxygen fills your blood hemoglobin and speeds tissue healing. It also helps in slowing down the growth of the bacteria.
Treating surgeon will need to find out what’s blocking your blood supply and treat that condition. Like incase of cardiac block one needs to get angioplasty done or in case of vascular disease like varicose veins or DVT one needs to get operated for clearing the blocked blood vessels.
Maggot’s treatment:
This method was practiced in olden days to remove the dead tissue in gangrene. Maggots still do play a good role in modern medicine. Your respective doctor puts maggots from fly larvae (specially bred in laboratory) on your wound, where they eat dead and infected tissue without hurting healthy tissue. They also help fight infection and speed healing by releasing chemicals or so called secretions that kill bacteria.
Antibiotics:
Intravenous or intramuscular antibiotics are given to the patient to control infection and septic conditions in gangrene. Also if the diabetes is high, insulin in monitored dose is injected either subcutaneously or intravenous drip to further control complications.
Hope after reading this article, one needs to understand the importance of monitored sugar in our life!!! Stay safe# Stay healthy!!!
Dont forget to share this article with your friends.