Hello everyone!!! Today Diabetes is so common that nearly 463 million people suffer from this disease globally. 1/3rd of the population with Diabetes suffer from cardiac problems. 1/4 th of the population suffering from Diabetes are treated with drugs beneficial in cardiovascular disease.
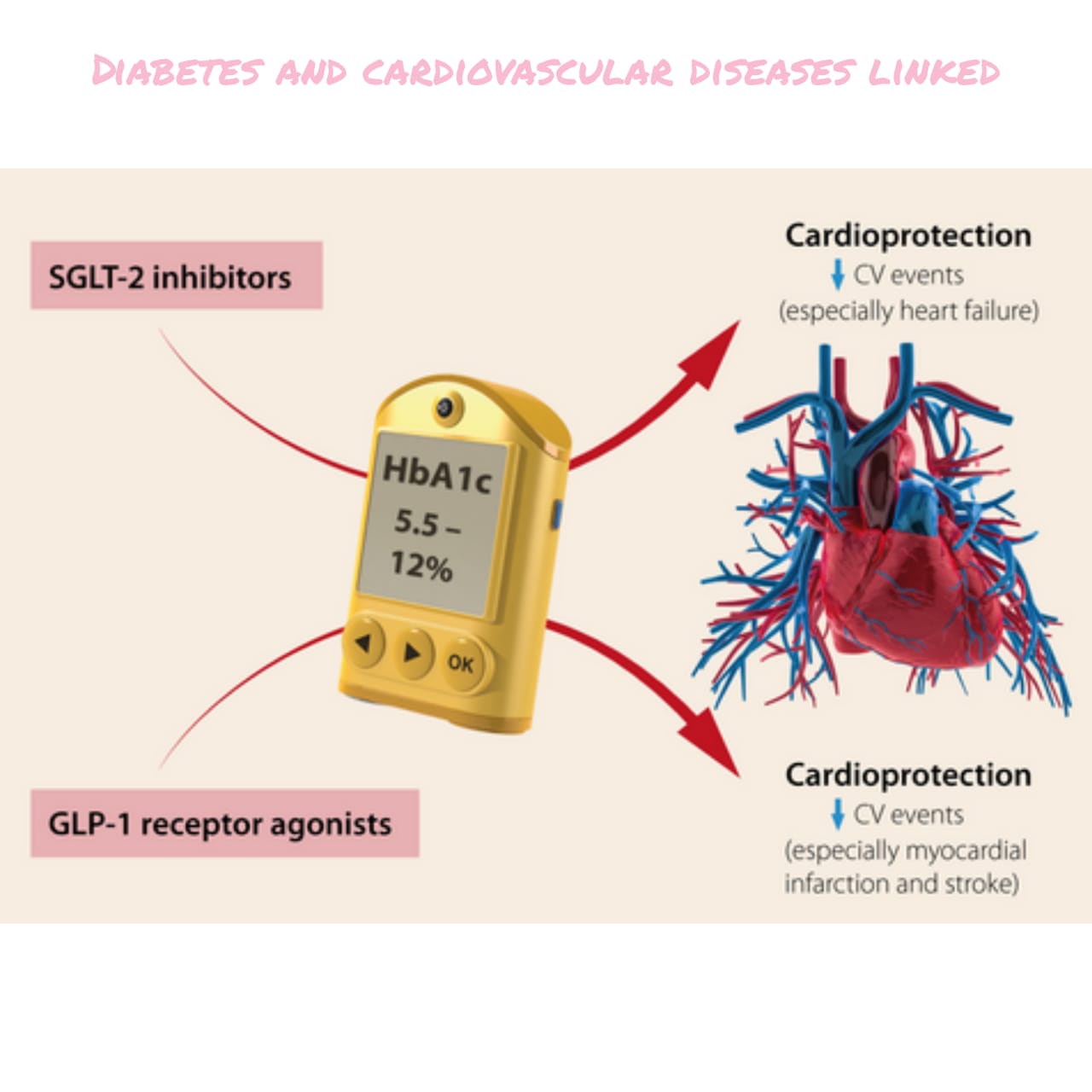
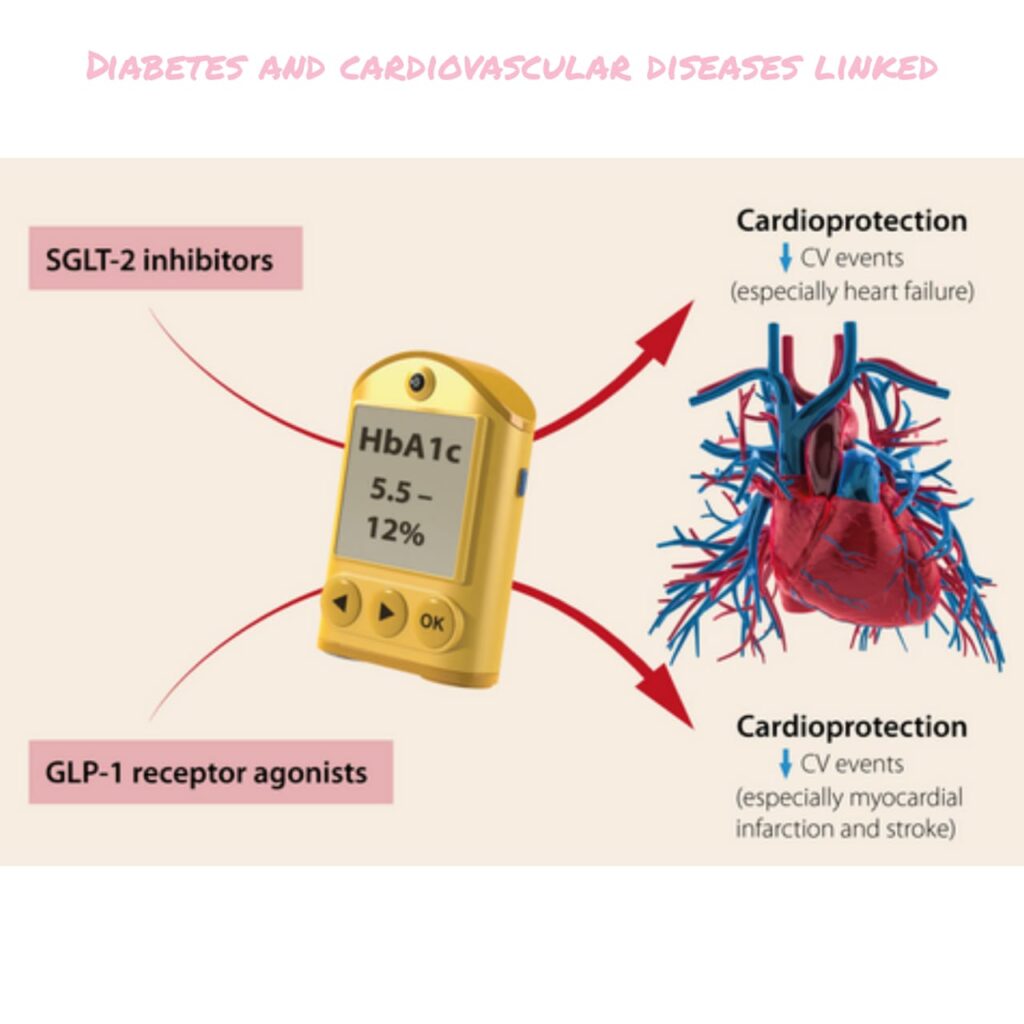
Do you know that Diabetes and cardiovascular diseases are linked? Well let me explain you the importance of role of treatment of Diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Risk factors for Cardiovascular disease with Diabetes:
- Increased blood sugar levels
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Alcoholism
- Stress
- Hyperlipidemia
- Obesity
All these above factors contribute to high risk for cardiovascular disease along with Diabetes. The prevalence of Diabetes with cardiovascular diseases are more in males than females. In US, obesity with Diabetes and cardiovascular diseases is very common.
Pathophysiology:
Increased blood sugar levels, high cholesterol levels (dyslipidemia) leads to blockage of arteries in heart by fatty deposits or calcium deposit in arteries causing cardiac blocks thus decreasing the cardiac output and cardiac function. Arteriosclerosis, coronary artery diseases, myocardial infarction, mitral valve stenosis are some of the conditions possible in such a scenario. Also insulin resistance plays important role in depositing glucose levels in blood thus making the blood thick and viscous. This decreases the flow of blood to heart thus hampering cardiac output. Heart Failure is commonly seen in Diabetes patients. Autonomic Neuropathy also plays a great role in heart damage or sudden cardiac death in diabetics. Also affecting glomerular filtration rate. This induces more of creatinine levels in blood. Thus Diabetes and cardiovascular diseases go hand in hand.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Breathlessness while walking or climbing
- Palpitation
- Chest pain
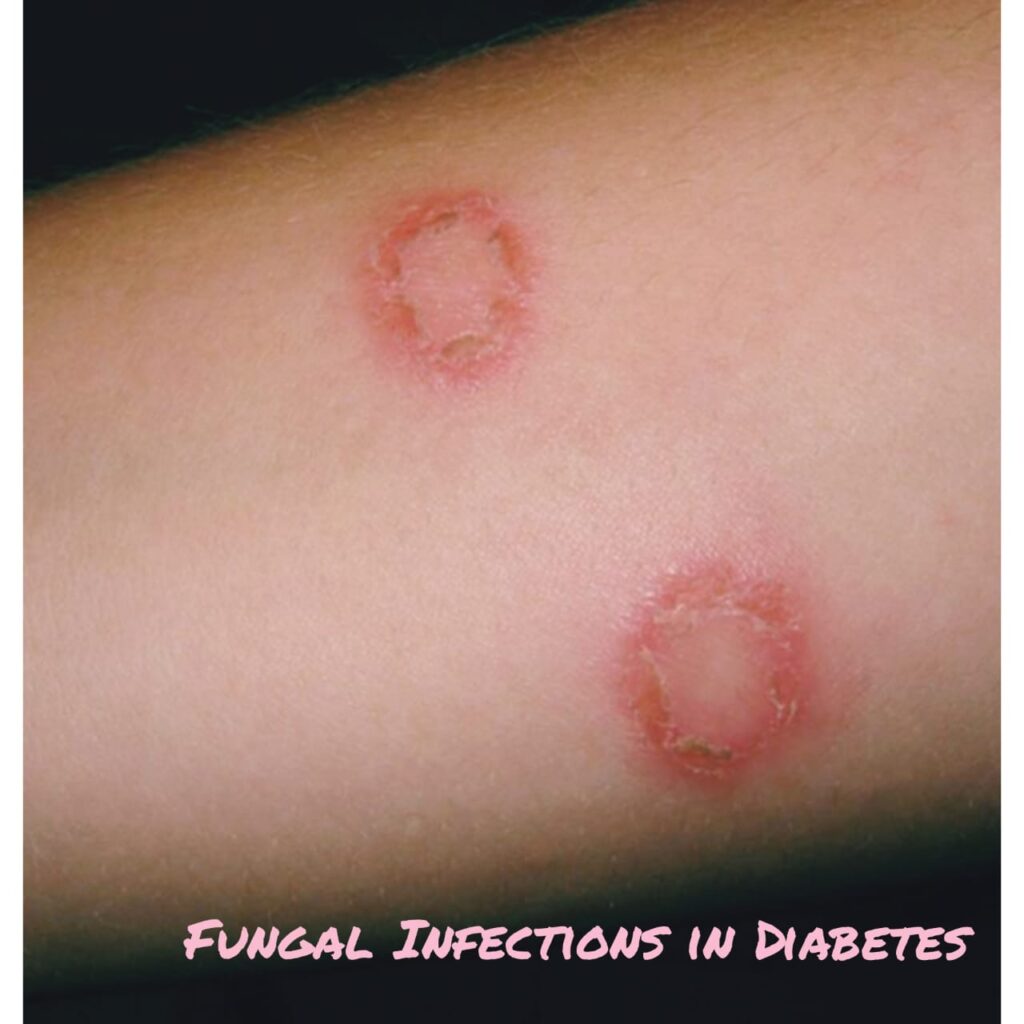
- Itching of the skin
- Burning urination
- Thirst for sips of water
- Headache
- Neuropathy
So after discussing these symptoms, we have well understood that controlling only Diabetes alone is not enough, one needs to take care of heart as well. So drugs controlling Diabetes along with cardiac problems are beneficial (Like SGLT2 Inhibitor, GLP1 Analogues etc).
Diagnosis:
- Increased blood glucose levels.
- Increased cholesterol levels, high LDL with low HDL levels
- High triglycerides
- High blood pressure
- Increased glycosylated hemoglobin
- Sugar in urine
- C- reactive protein increased
- Cpk levels increased
Management:
- Improving life style by avoiding junk food, eating healthy diet are of key importance.
- Daily exercise for half hour or brisk walk daily for an hour.
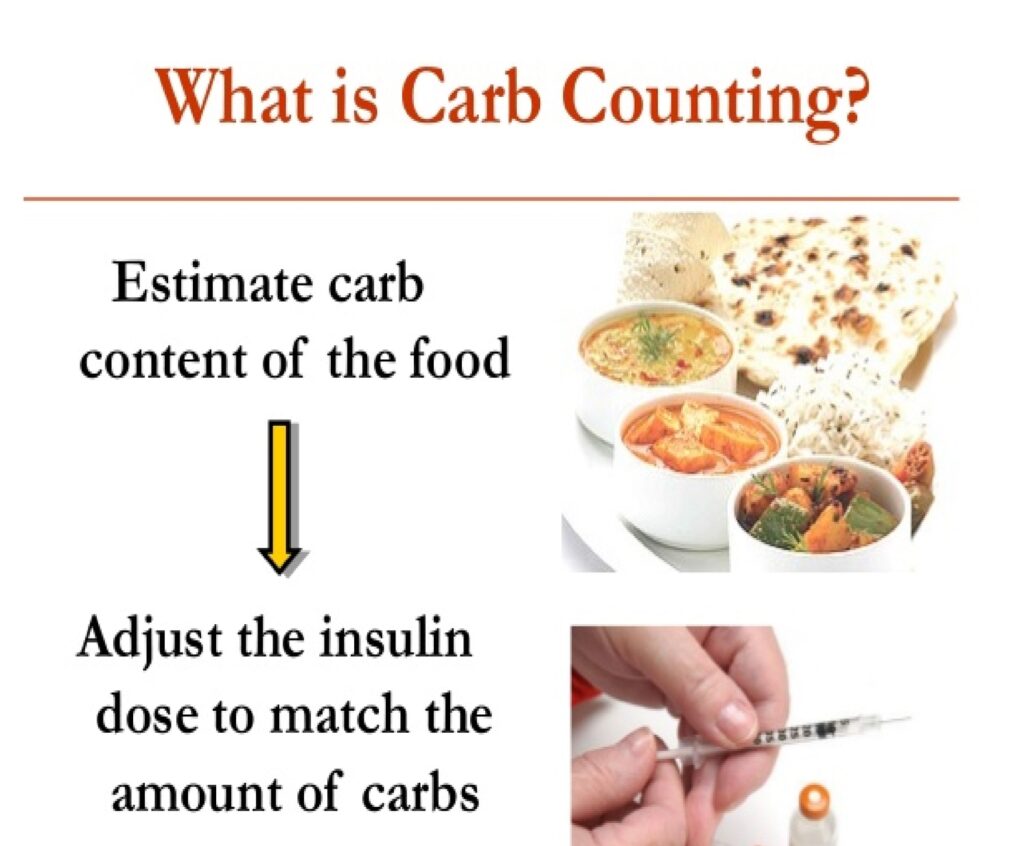
- Eat high fiber, low fat and low glycemic index food like pulses, Dals, legumes, egg white, low carbohydrate diet, fruits with low glycemic index like apple. Avoid eating rice and potato which are rich in carbohydrates.
- Avoid fried oily food.
- Monitor your glucose levels every 2 to 3 days at home and plan your meals accordingly so as to avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Plate diet in Diabetes is very important to follow.
- Cinnamon boiled in warm water intake to decrease cholesterol levels.
- Methi seeds soaked in water. Drinking this water helps reduce blood sugar levels.
- Regular health checkups with your concerned diabetologist every 3 to 6 months and also a follow up with your cardiologist or family physician is required.
- DPP4 Inhibitors Like Sitaglipltin, Linagliptin etc and Metformin are the drug of choice in Diabetes Mellitus which do not cause hypoglycemia especially in elderly.
- Statins like Rosuvastatin, atorvastatin are used to control cholesterol.
- Beta blockers, Angiotensin receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers like Atenolol, Telmisartan, Amlodipine etc required for treatment of heart disease and high blood pressure.
- Yoga, meditation helps in releasing stress and improving the sleep patterns.
Hope you all have understood the importance and role of Diabetes in cardiovascular diseases and Diabetes and cardiovascular diseases are linked. Thank you for reading and have a healthy and safe life.