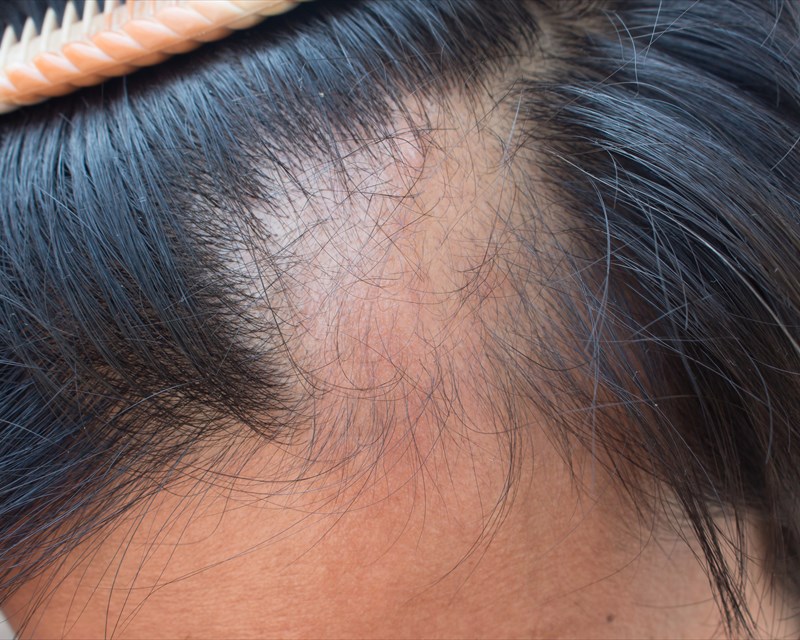
Diabetes and Aloplecia are usually linked but very rarely discussed. Nearly 45% of the Indian population faces Aloplecia areata due to Diabetes and other causes.
There are various causes of Aloplecia as follows:
- Diabetes Mellitus especially type 1.
- Hypothyroidism
- Stress
- Hormonal imbalance
- Iron deficiency anaemia
- Hereditary
image credits: yalemedicine,org
Diabetes:
Usually Type 1 Diabetes leads to significant hair loss. When blood sugar levels in your body are uncontrolled, it results in significant changes and damage to the blood vessels. This results in poor oxygen supply to smaller blood vessels leading to damage to the hair follicles. Usually, in normal hair growth cycle, due to anagen catagen activity, the hair falls in the final cycle after which the new hair grows from the hair follicles. But due to uncontrolled Diabetes, the immunity hampers the growth of new hair follicles and thus resulting in patches of baldness. In Type 2 Diabetes similar effects do occur but generally are less extensive.
Hypothyroidism:
Due to endocrine imbalance, there is increased TSH levels and decreased thyroxine production leading to imbalance in hormonal levels. Thus leading to hair loss.
Stress and hormonal imbalance:
Both stress and hormonal imbalance goes hand in hand. Increased stress levels results in Anxiety which in turn disturbs sleeping pattern of an individual resulting in imbalance in hormonal levels . This affects the growth of hair follicles and leads to hair fall.
Iron deficiency Anaemia:
Due to decreased iron in haemoglobin, decreased hemoglobin count resulting in anaemia.
Heriditary:
Genetic cause is ofcourse not ruled out. Aloplecia in early aged population is usually hereditary.
Thus all these factors affect the hair follicle resulting in hairfall and leaving patches of baldness.
But Type 1 Diabetes, usually affects the anagen catagen phase in a more severe manner, affecting the immune response. So there is loss of hair overall like the scalp, over eyebrows, over chest etc. In Insulin resistant cases, hairfall occurs faster due to damage to the hair follicles.
Management and treatment of Diabetes and Aloplecia:
- One must monitor and control Diabetes so as to keep the cause under control to control hairfall. In type 1 Diabetes, insulin injections along with medication usually help to control autoimmune Diabetes. Regular checkup with your diabetologist usually helps in monitoring your blood glucose levels.
- Patches of Aloplecia are usually tackled with Minoxidil tab orally and also local application.
- Apply onion juice or aloe vera juice locally over the affected area for months together is often of great help (I don’t recommend but some found it useful).
- Improvement in lifestyle changes benefits an individual to avoid stress and improve good quality sleep.
- Keeping a check on thyroid hormones, like treatment for Hypothyroidism helps. Eltroxin (Levothyroxin) tab orally helps to keep a check on Hypothyroidism and obesity.
- Using proper sulphate free shampoo and regular oiling your hair helps to a certain extent for hair growth and prevents dandruff.
- Ofcourse Tricology has advanced souch in this field of hair grafting which is of help to cover certain patches of hair.
- Multivitamins like B complex, Vitamin E and Biotin helps in growth of the hair follicle and prevents hairfall.
- Trace elements like selenium, zinc, etc and vitamin D suppliments found out to be having a good effect on hair growth.
I’m sure most of the Diabetics especially type 1 must be facing this problem but is hesitant to discuss it due to scalp shaming and ignore it unless very severe patches are shown. Hope the significance of hairfall, it’s causes is well understood and it’s correlation with Diabetes!!!
Have a great day!