Diabetes and Hair loss: An Underrated Connection
Introduction:
Diabetes is a lifestyle illness that stays with you for life. The correct phrase to describe it: give it an inch and it’ll take a foot. Rightly so, diabetes is like a termite that infests every body part. Extensive research in the last decade has concluded that “HAIR” is the new mirror for diabetes. Hair can reveal a lot about the disease’s activity.
We are too worried about diabetes affecting the foot, the fingers, the nerves, and the eyes, but what about the hair? Is it vanity to draw this comparison? Trust me, no. The study of molecular hair has opened up new avenues for diagnosing diabetes and its complications. We also need to understand how to stop hair loss from diabetes.
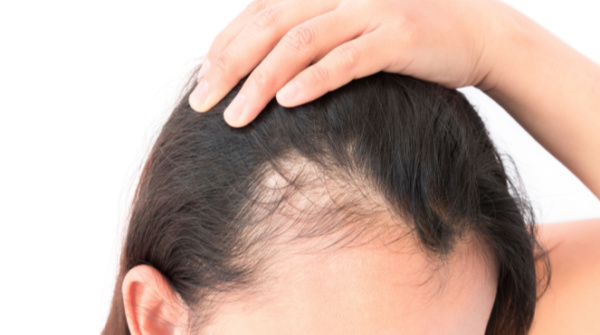
What is hair loss?
At any given time, approximately 90% of the hairs on the scalp are in a growing phase. About 10% of the hairs are in a resting phase. After 2 to 3 months, the resting hairs enter the telogen phase, or the shedding phase, followed by new hair growth in their place.
Type 2 diabetes and hair loss:
Can type 1 diabetes cause hair loss? Yes, type 1 and type 2 diabetes can both cause hair loss in men and women.
Type 1 diabetes: Alopecia (baldness), like type 1 diabetes, is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissue. This can attack developing cells and hair follicles in the scalp, brows, eyelashes, and elsewhere.
Type 2 diabetes: Hair loss is a common side effect of type 2 diabetes because of poor blood circulation in the body. To grow hair, we need plenty of oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to reach our hair follicles.
Diabetes, on the other hand, can make capillaries and other larger vessels fragile and weak. Their efficiency in carrying blood to all parts of the body is compromised. Apart from the scalp, hair loss on the legs, feet, and arms is an evident sign of diabetes type 2. You tend to loose your eyebrow hair as well.

Causes of hair loss in diabetes:
- Fragile blood vessels:
Small blood vessels like capillaries become weak, and fragile and lose their tonicity when blood sugar levels are high. Because of this damage, less oxygen and inadequate nutrients are supplied to the hair follicles, causing the hair to thin. This also causes your hair to lose its shine, appearing brittle, dry, dull, and lifeless. So, does diabetes cause dry hair? Yes, it sure does.
- Deranged thyroid hormones:
Hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disease that can cause significant hair loss in patients with type 1 diabetes.
- Anemia:
Anemia is not caused by diabetes directly, but certain complications and conditions associated with diabetes can contribute to it. Diabetes-related kidney disease (nephropathy) and nerve damage (neuropathy), can both lead to the development of anemia. Furthermore, taking certain oral diabetes medications for diabetes can increase the risk of developing anemia.
Anemia directly causes poor oxygen supply to body cells, affecting hair growth rate.
- Alopecia areata (autoimmune):
As explained, type 1 diabetes and alopecia are both autoimmune diseases. The disease wreaks havoc on the body’s tissues. This can result in an attack on growing cells and hair follicles in the scalp, brows, eyelashes, and all over the body.
- Stress:
Diabetes causes physiological as well as psychological stress and anxiety. Stress and anxiety are both direct causes of hair loss. Dehydration is also a factor.
Frequently asked question: insulin resistance hair loss reversible?
If your blood sugar levels are not controlled with medical treatment, hair loss from type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance can be permanent. Patients who keep their blood sugar under check with medication, dietary measures, and regular exercise, on the other hand, have much better outcomes. There are chances of restricting balding.
How to control hair fall in diabetics:
- Blood sugar management
It is critical to improving your blood sugar levels. Following the American Diabetes Association’s recommendation of keeping your HbA1c at or below 7%, will improve your overall health and prevent numerous diabetes-related complications, hair fall being one of them.
A count of less than 6.5 percent will ensure better health of the blood vessels and prevent the growth of fragile capillaries from reducing blood supply to the hair follicles. But this requires an aggressive approach to blood sugar reduction.
- Medications
To be prescribed strictly by the physician or Diabetologist. Drugs like minoxidil (topical application) and finasteride (only for use by males) are widely used to induce hair growth.
- Exercise
The best exercises are walking, swimming, calisthenics (body strength exercises using your body weight), and yoga. These are the best methods to rush oxygen to all body parts and boost metabolism (better digestion and absorption of food will in turn reduce blood sugar levels).
- Biotin
Biotin levels in diabetics may be lower than recommended. Also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, it helps to slow hair loss in people who are deficient in it. Adults should consume 25 to 35 micrograms (mcg) per day, but supplements typically contain much higher amounts. Peanuts, almonds, potatoes, oats, onions, and eggs are natural biotin sources.
- PRP
Platelet Rich Plasma is created by drawing blood from a patient and spinning it down. The plasma is then extracted. It is a concentrated version of platelets. It contains growth factors that can help stimulate the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles.
- Hair transplant
Hair or follicle transplants may not be a long-term solution.
- Wigs
Essentially, false hair is a purely aesthetic option.
Conclusion:
Did you know that science now allows the diagnosis of diabetes through hair loss?
If a person is losing more hair than usual and the loss does not appear to follow a typical pattern of hair loss, a doctor must be consulted. Diabetics have thinner hair than non-diabetics. Diabetics have a significantly reduced hair shaft diameter.
Known fact: HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin) is proportional to the average blood glucose concentration over the previous four to three months.
But did you know?
Keratin and other hair proteins are glycated as well. The levels of glycosylated keratin in hair can also be used to determine the onset of diabetes. Interesting, isn’t it?
I hope you like this article.
if you have any queries, please ask them in comments
for more info subscribe to our YouTube channel and Facebook pages.
have a great Day!