Diabetes when uncontrolled, leads to increased chances of fungal infections. About 20 percent of India population suffers from fungal infections of the foot. Both Diabetes and fungal infections are linked with eachother. When the blood sugar levels are increased, there is increased growth of yeast resulting in fungal infections. The most common fungal infection is caused by Candida albicans (Yeast). Diabetes affects each and every part of the body, especially the skin. The first sign or symptom appearing is itching of the skin, especially the vagina in women. The most common skin symptoms include diabetic dermopathy, diabetic blisters, eruptive xanthomatosis and necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum.
Many bacterial infections of skin include stye (infection of glands of eyelid), carbuncles, furnuncles, folliculitis (infection of hair follicles) etc. The most common bacterial infection is staphylococcus bacteria. Fungal infections like Candida albicans are yeast-like fungus which create itchy rashes of moist, wet, red areas surrounded by tiny small blisters and scales. These infections occur in warm and moist folds of the skin. Most common regions are under the breasts, around the nails, between fingers and toes, in the corners of the mouth, under the foreskin of penis (in uncircumcised men), and under the armpits and groin.
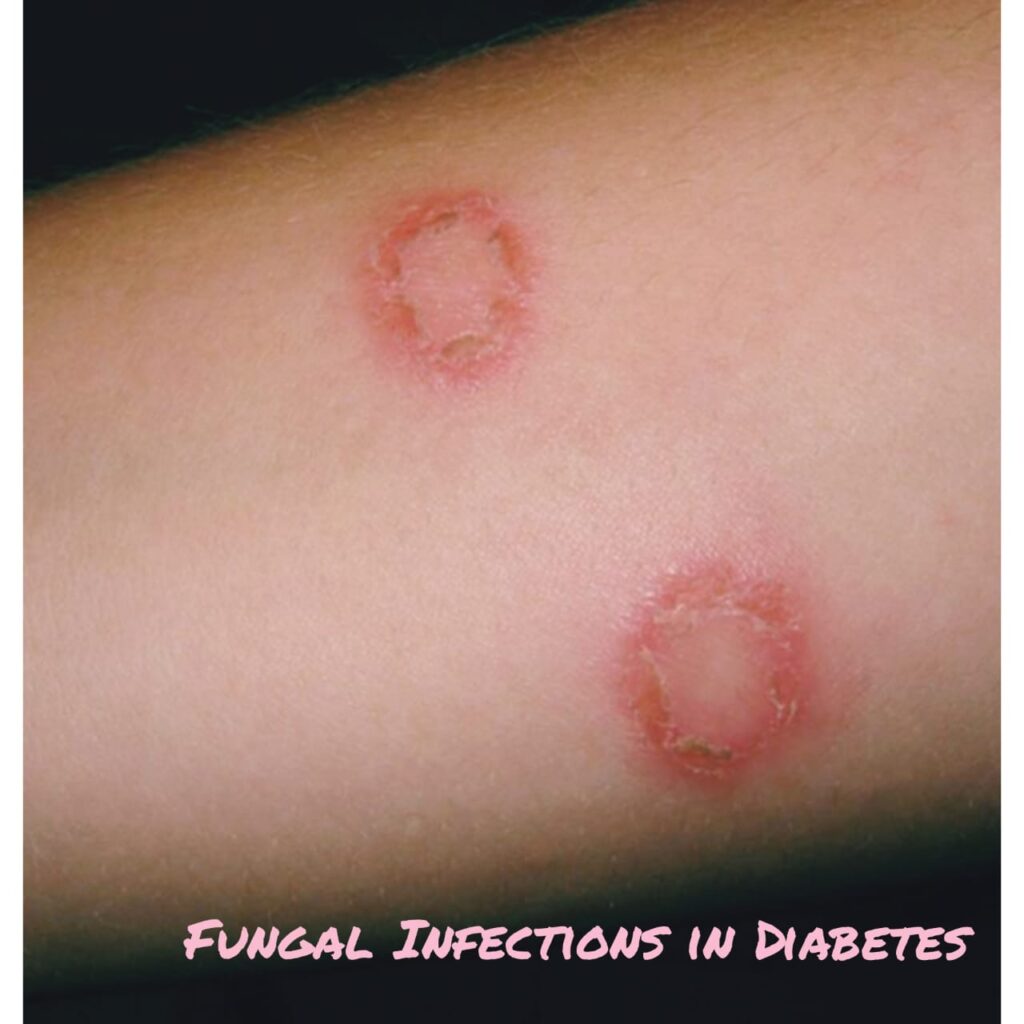
Common fungal infections include ringworm (a ring-shaped itchy patch), jock itch, athlete’s foot and vaginal infection that causes itching.
Severity of these fungal infections varies from asymptomatic-mild mucocutaneous infections to life threatening systemic infections.
Factors contributing to Fungal infections:
The main determining factors of fungal infections are linked to geographical and socio-economic characteristics and increasing number of at-risk populations. Patients susceptible to fungal infections include those with immunosuppressive illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, chronic pulmonary diseases (COPD), tuberculosis, cancer and diabetes. It has been observed that patients with systemic fungal infections are at high risk of developing disseminated fungemia and prolonged stay in hospital. This condition is worsened if the patient has a metabolic disorder due to diabetes mellitus. This is because the diabetic patients are more prone to high blood sugar concentration which weakens the immune system and causes several other health complications.
There is high risk of fungal infections in individuals suffering from Diabetes Mellitus. Also it is difficult to treat fungal infections when the blood sugar levels are high.
Pathophysiology:
Usually there is presence of yeast in skin and mucous membrane. But when the blood sugar levels are high, yeast multiplies and form colonies which stick to the skin and mucous membranes. This leads to fungal infūections. There is itching, pain and inflammation of the skin in moist and wet regions.
In type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, the immune system is weak resulting in highl risk for fungal infections especially of foot. When the blood sugar levels are high, the extra glucose is excreated in mucus, urine and sweat. Once the yeast has formed colonies, it’s easier for the fungal infections to return.
Sites of infection:
In women with high Diabetes, the vagina and folds below breast are the common site where there is itching, with foul odour, vesicles formed.
In men, penis is the common site of infection.
Foot infections are very common for fungal Infections.
Eye infections with discharges, blurring of vision, itching and pain in eyes.
Oral thrush, with white patches in mouth, loss of taste, burning and cottony sensation in tongue.
Management:
Usually the patient is examined for the affected area of the skin and prescribed antifungal topical application and suppositories as well as oral medication like fluconazole, Itraconazole, cotrimazole, Miconazole, luliconazole and in severe infections even variconazole. Also Diabetes is also kept under complete check.
Now a days Many Diabetologists have noticed that the resistance to antifungal drugs is increasing day by day and even after using a combination of 2 or sometimes 3 antifungals not able to control the infection.
Also local hygiene is also maintained of the affected area. Diet is also monitored.
In resistant cases personal hygiene play an very important role. fungal spores are not easily destroyed so merging cloths in boiling water and changing bedsheets every alternate day. not using same cloths again without washing. not sharing cloths. breaking scratch-itch-scratch cycle by anti allergic medication. keeping genital area free of moist and clean plays a pivotal role.
Hope this article clarifies your doubts and queries regarding the Fungal infections in Diabetes.
i will soon write a new article on Ringworm infection and white discharge through PV soon.
if you have any queries drop me a meassage in comments here or on Youtube.







Usefull information, Thankyou