Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) is also known as Diabetic kidney disease. DN leads to chronic loss of kidney function due to diabetes mellitus. Over 45 percent of cases of kidney failure are caused by diabetes, and it’s estimated that approximately 190,000 people are living with kidney failure caused by complications of diabetes. When the blood sugar levels are increased, there is progressive damage to the kidneys.
Diabetic nephropathy is one of the causes of end stage kidney disease. The kidneys regulate the levels of salts and fluids in the body, which is important for controlling blood pressure and protecting cardiovascular health. In ESRD, the kidneys donot work well enough to meet the needs of daily life. This leads to kidney failure due to failure in filtration of salts and fluids.
Pathophysiology:
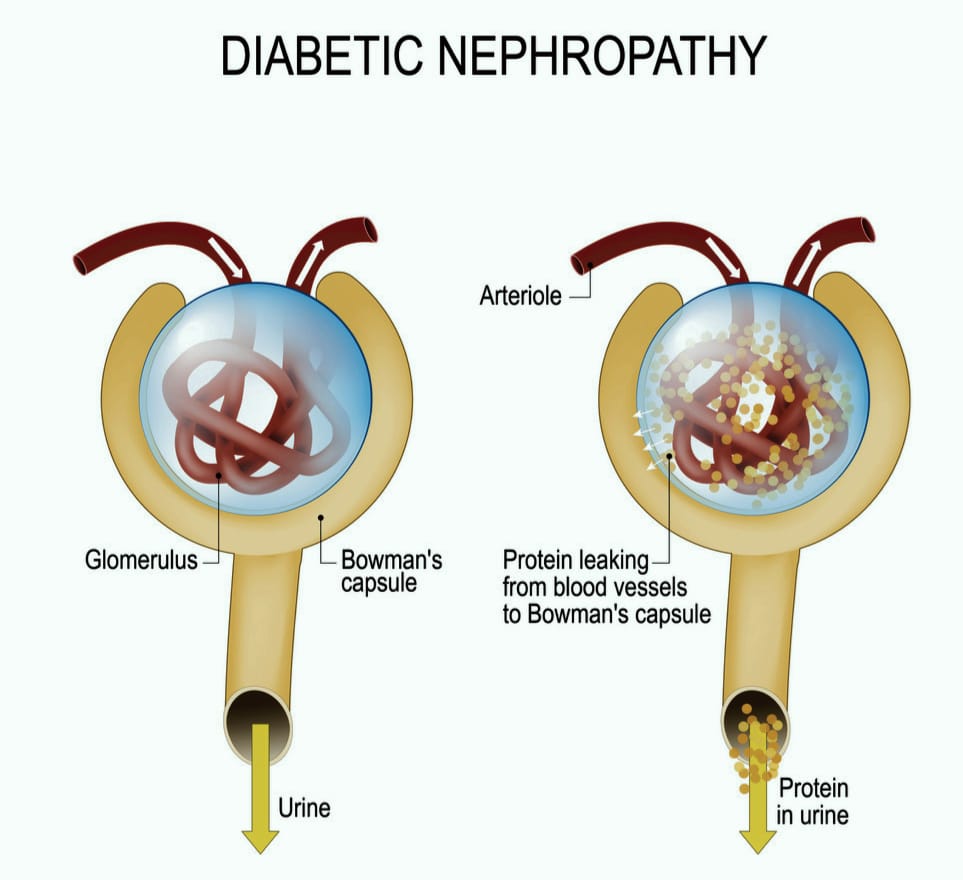
When our bodies digest the protein we eat, this process creates waste products. In the kidneys, millions of tiny blood vessels with even tiny holes in them act as filters. As blood flows through the blood vessels, small molecules such as waste products pass through the holes. These waste products become part of the urine. Useful substances, such as protein and red blood cells, are larger in size do not pass through the holes in the filter and stay in the blood. High blood glucose levels interfere with the function of the glomerulus. The filter function of the kidneys get damaged and proteins start to leak from the blood into the urine. Albumin being the smallest of proteins goes first hence by measuring its presence in urine we can measure the damage to kidneys.
Symptoms of Diabetic Nephropathy(DN) :
- Albumin in urine
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Drowsiness/ disturbed sleeping pattern
- Dryness of skin and itching
- Stomach upset
- Swelling of face, feet and hands.
- Loss of appetite
- Uremia due to retention of waste products.
Risk factors:
People who have diabetic nephropathy also often have high blood pressure. High blood pressure can further contribute to kidney damage. High blood pressure lead to increase in filtration pressure and can further lead to pores wide open. under high pressure it increases the chances of albumin to slips into the urine and increasing the kidney damage further. so controlling blood pressure is essential to halt kidney damage.
Other risk factors include obesity, smoking, alcohol, hereditary and people suffering from cardiovascular diseases. Diabetic nephropathy is a complication of uncontrolled Diabetes mellitus and usually accompanied with diabetic neuropathy and diabetic retinopathy.
Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Nephropathy(DN) :
- X ray kidney ureter bladder (KUB) can help in detection of any damage to the kidney.
- CBC, ESR, Urine routine and C reactive protein are some of the tests which can help in detecting the nephropathy.
- Also Blood sugar levels should be monitored at regular intervals.
- Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) gives an indication of the kidney function to filter waste products from your blood.
- Albumin / Creatinine ratio or 24hr albumin in urine is another important test.
Treatment for Diabetic Nephropathy:
Early detection and treatment of diabetic nephropathy can not only stop the progression of kidney disease, but during the early stages can actually reverse it. Treatment involves controlling both your blood glucose levels and your blood pressure. ACE inhibitors and ARBs are the class of drugs which helps in restricting the kidney damage by reducing those pores size by altering the renal glomerular blood vessels flow (afferent and efferent arterioles) and preventing albumin loss. CKD is not reversible as such but we can obviously delay its progression.
Oral medication usually helps in controlling diabetes. Also insulin injections are given when the sugar levels are out of the limits.
Lifestyle changes are a must for a healthy normal life. Working on your obesity is equally important as per body mass index.
Quiting smoking and drinking alcohol usually improves the overall wellbeing of an individual.
Plate diet plan helps often in improving the condition of the patient. Avoid seedy foods like lady’s finger, tomato, seedy foods are a must to consider. A reduced protein diet can help to prevent Diabetic nephropathy this preventing protein in urine.
Exercising regularly for half an hour is a must to vent out energy and utilize extra glucose. (not advisable in last stages)
In last stages salt restriction and water restriction plays an important role in its progression.
If you like this article do share it with friends and family.
have a great day.