HbA1c or Glycated Hemoglobin is most reliable test for confirming diabetes. HbA1c measurement has a central role in management of diabetes. HbA1c levels can be directly related to the risk of development of diabetic complications.
What is HbA1c (Glycosylated Hemoglobin) ?
Hemoglobin in blood reacts spontaneously with glucose to form glycated derivatives in a non enzymatic manner. The process occurs slowly, with the extent of glycation determined by the concentration of glucose in the blood. Human hemoglobin A undergoes such glycation to form HbA1c from a reaction between the Beta chain of hemoglobin A0 and glucose. Other compounds result from similar reactions on the alpha and beta chains of hemoglobin and these can be measured as the total glycated hemoglobin.
Which conditions affect HbA1c levels ?
Glycated hemoglobin can be affected by the presence of hemoglobin variants and uremia. Vitamin C, Hemolytic and Iron deficiency anaemia can also give abnormal results. Other conditions in which there is a rapid turnover of red blood cells ( e.g. polycythemia, anaemia or blood transfusion) can also give inaccurate results.
Why HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin) is most reliable test for Diabetes ?
HbA1c (Glycated Hb) serves as a retrospective indicator of the average glucose concentration over the previous 6-8 weeks. Approximately 50% of the variance in HbA1c is determined by the average blood glucose concentration over the previous month. 25% by the concentration over 30-60 days, and the remaining 25% by the concentration from 60 -120 days ( Red blood cells have lifespan of around 120 days).
- HbA1c offers a potentially easier, non -fasting and therefore more acceptable test.
- There is less intra individual variation with HbA1c than glucose testing. ( Fasting blood sugar test can vary in intra individual depending on hours of fasting, quantity and quality of food consumed )
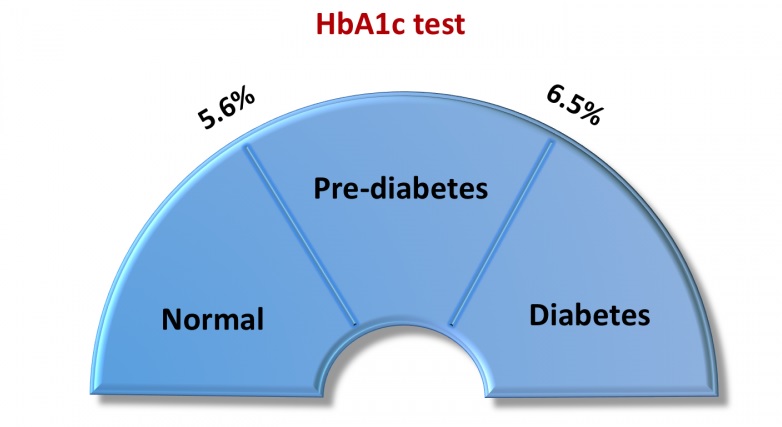
How HbA1c is interpreted ?
Results of HbA1c can be interpreted for diagnosis of diabetes as :-
5.6 % and below = Normal
5.7 – 6.4% = Pre-diabetes
6.5% and Above = Diabetes
At the time of diagnosis if you have HbA1c of less than 5.7 % that means you do not have diabetes (excluding conditions affecting HbA1c readings mentioned above). If your reading is between 5.7% -6.4 % then you are in Pre-diabetes stage i.e. you have risk of developing diabetes. At this stage diabetes can be reversed to normal with diet, exercise (weight loss) and certain medication which enhances insulin sensitivity. 6.5% And above HbA1c indicates established diabetes. If your blood sugars are in Pre-diabetes range or established diabetes range then consult diabetes specialist immediately.
In already established diabetic person HbA1c monitoring helps diabetologist to check the control of blood sugar in preceding 3 months and can titre medication according to it.
According to ADA guidelines HbA1c of < 7 % is the goal for diabetes management. In younger patients tight control (HbA1c of 6.5%) is even better in minimizing the complications of diabetes.
It has been proven by DCCT & UKPDS trials ( Type 1 & 2 diabetes patient study) that reduction in HbA1c even by 1 % reduces majority of microvascular complications ( retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy) & macrovascular complications ( peripheral vascular disease, amputations, heart failures).
HbA1c is also used for monitoring sugar control progress during pregnancy.
That was all about HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin) and its use.
If you like my article please share it with your friends and family.
Awareness is prevention !