Bad breath and bleeding gums—are your sugar levels high?
Introduction:
Diabetes—a deadly disease with roots that spread far and wide. Diabetes has countless effects, all of which last for a very long time. India is regarded as the “diabetes capital of the world” due to the alarming increase in diabetes diagnoses among the younger population. The most recent study has focused on the unavoidable link between diabetes and oral health.
Can diabetes affect your teeth?
Not just your teeth, diabetic gums is also a pestering issue. Diabetes has an impact on every organ in the body, including the skin, gut, kidney, heart, nervous system, eyes, and mouth. People are aware that diabetes can result in heart disease, coma, blindness, and kidney failure. Few people, however, are aware of the link between diabetes and oral health. A diabetologist-dentist partnership is necessary to help patients with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes teeth and gums.
Let’s understand how diabetes affects our mouths.
Diabetics are more likely to experience dental issues for the following reasons:
- Bacteria that cause cavities thrive in conditions of increased salivary sugar brought on by high blood sugar. On the other hand, infections from soggy bleeding gums and decayed teeth can cause the blood sugar to rise and make it harder to control diabetes. It’s a vicious cycle. The faster you understand this, the better you can address the problems.
- Diabetes alters the blood vessels. They are thickened, become frail, and also grow in numbers rapidly. These vessels do not supply the blood with the same efficiency as the normal ones. The nutrient supply is poor, and the cleansing action is inadequate. This reduced blood flow can cause diabetic gum and weak bones, putting them at a greater risk of infection.
- Diabetes medication reduces oral salivation. Cavities develop when the enamel is exposed to different acids in food and beverages due to dry mouth. Dry gums are sore, attract tartar, and can bleed on exposure to anything hard. ‘Does metformin affect your teeth?’ Well, now you have an answer!
Diabetes mouth symptoms:
Do you have oral issues and suspect an underlying increase in blood sugar? Let’s find out.
Keep an eye on your oral health while eating and brushing. Watch out for the following signs:
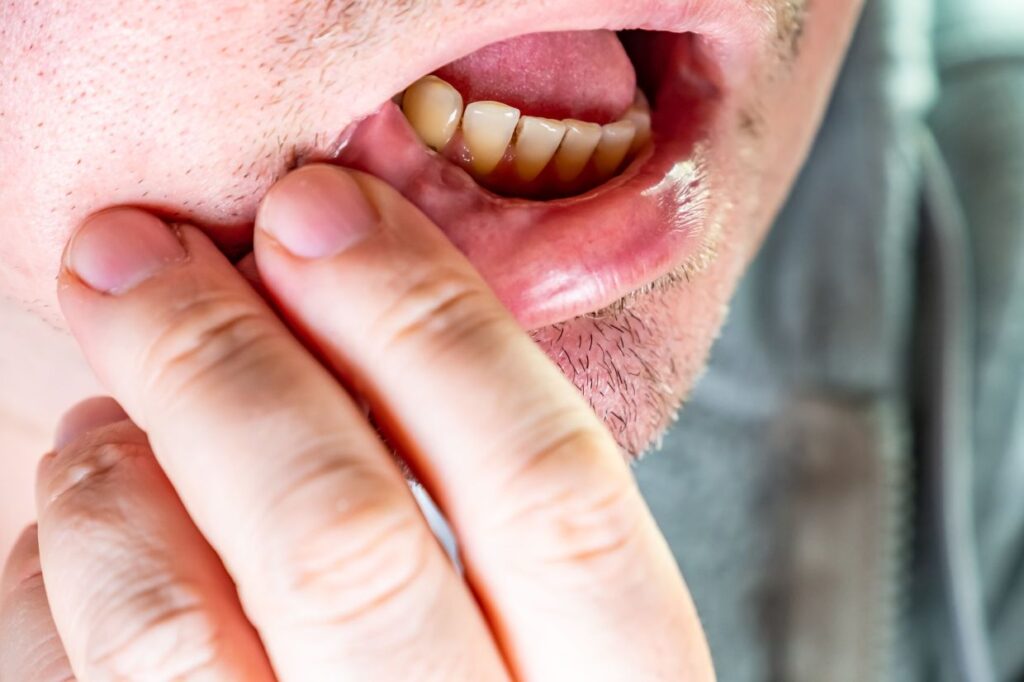
- Sore, reddish, bleeding gums.
- Dull, boring, nagging jaw pain.
- Receded gums; gums that pull away from the teeth.
- Hypersensitive teeth
- Salty taste
- Bad breath
- Shifting of teeth causing spacing
- Dry mouth, causing burning sensations.
- Food getting stuck at odd places
- Development of pimple-like abscesses that resolve and recur spontaneously.
What should you do if you notice these diabetes mouth symptoms?
Visit your diabetologist first and then a dentist. Dental treatment requires sugar levels to be within a certain range (HbA1c within 7). Dental procedures performed with high sugar levels pose risks of cross infection, pneumonia, and endocarditis.
The diabetologist performs all necessary investigations to tap the root cause of any spike in the blood sugar. These could be
- Uncontrolled foods and beverages.
- Lots of sugar intake
- Lack of sleep
- Lots of coffee
- Dehydration
- Tolerance to diabetes medication
- Dental issues.
Once the diabetologist has redone your prescription and changed your diet, he will closely monitor your blood sugar levels. Once it begins to subside, you can visit the dentist and start the required dental procedure.
Home appliances for sugar monitoring come in handy in such cases.
Diabetes gum disease treatment:
Now that we know that diabetics are susceptible to dental infections, especially the gums, let us begin with what you can do as a diabetic to prevent oral diseases from happening.
- Monitor your glucose daily, and be disciplined with the prescribed medications. The market has plenty of authentic, FDA-approved gadgets to monitor blood sugar. Sugar-free, sweet substitutes are a great way to control your sweet tooth. Stop indulging, and you will see the results shortly.
- Diet: Reduce foods that spike blood sugar and hydrate yourself well. Include a lot of fiber-rich foods, for instance, raw fruits and salads.
I would suggest an entire fruit over juices and shakes. Fiber is important to boost metabolism and counteract sugar. Green salads keep you full for a longer period, prevent frequent snacking, and also add bulk to your bowels. Apart from all the raw micronutrients that you receive from them, the sugar levels are also controlled.
Fibrous foods naturally scrub plaque and residues from the tooth and gum surface, keeping it clean.
- Drink plenty of water. Hydrate yourself well. Dehydration concentrates the blood, thereby causing sugar spikes. It also reduces saliva flow in the mouth making the enamel susceptible to decay and the gums sore.
- Before going to bed, make sure to brush. Brush twice daily. Do not indulge in midnight munching after that.
- Don’t forget to brush your tongue after you’ve brushed your teeth. The white tongue coating can be removed using a tongue scraper. Fungal infections on the tongue are very common in diabetics. They present as white patches.
- Repeat the three steps of floss, rinse, and repeat after each meal to remove any food particles. The toothbrush will not clean minor food residues from between the teeth. This is a leading cause of gum pockets and bone loss. Be thorough with your hygiene.
- Water flossers are highly sophisticated oral hygiene devices. They use a strong water jet to flush out any loose dental plaque.
- Mouthwashes: These are liquids that take care of sustainably releasing disinfectants in the mouth. Chlorhexidine, an ingredient in mouthwash, keeps gums healthy.
- Make sure to rinse your mouth after taking a vitamin gummy or cough drops/lozenges. Gummies with no added sugars are available these days and are safe for diabetics.
- Smoking and diabetes are a bad combination. Curb your cigarettes or nicotine intake of any sort.
Conclusion:
Stop contemplating! Do not wait until diabetes-related gum disease gets so bad that you lose all your precious teeth. Understand that maintaining good oral health will also help you control your diabetes and avoid health issues linked to it. It will be more challenging for you to follow a healthy meal plan if you have dental problems that result in tooth loss. Value the smile while you still have healthy teeth.