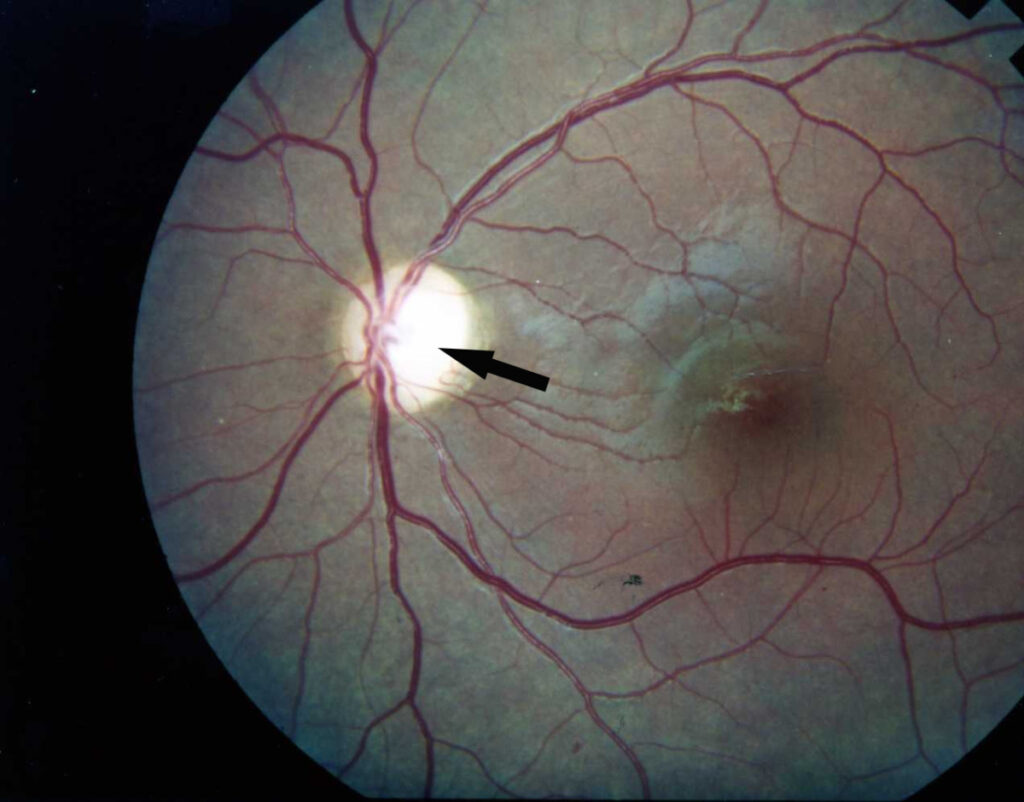
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a complication of uncontrolled diabetes which causes damage to the blood vessels of the retina which is placed behind the eye.
This condition can lead to blindness if not treated at the correct time. Regular eye checkups can prevent early blindness. Effective management of the diabetes plays a key role to prevent Diabetic Retinopathy. It is the most common cause of blindness in the United States.
The retina is the membrane that lies at the back of the eye which is highly sensitive to light.
It converts any light (image) that hits the eye into signals that can be read by the brain. This process produces visual images and this is how a person sees.
Diabetic retinopathy damages the blood vessels within the retinal tissue, causing the fluid to leak and distort vision.
Symptoms :
Blurred vision, difficulty seeing and recognising colors, loss of night vision, floaters or dark rings in front of eye and even total loss of vision.
Types:
There are two types of Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR): Symptom less and milder for of DR.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): PDR is the advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy in which there is formation of new, abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
Approximately around 5.4 percent of people in the U.S. aged over 45 years have DR
People suffering from diabetes should have their eye sight checked at least once in a year to rule out DR. The retinal surgeries help reduce the symptoms by controlling diabetes and management of early symptoms are the most effective ways to prevent Diabetic Retinopathy.
Causes and trigger factors :
A person suffering from diabetes is at high risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- High blood pressure
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Hypercholestreamia
- Pregnancy
- smoking regularly
- Chronic diabetes
Complications:
Complications associated with diabetic retinopathy include:
- Vitreous hemorrhage: This occurs when a newly formed blood vessel leaks into the vitreous gel that fills the eye and stops the light from reaching the retina. The patient experiences symptoms like loss of vision and sensitivity to light, or floaters in milder cases. This complication can resolve on itself if the retina remains undamaged.
- Retinal detachment: Formation of scar tissue which pulls the retina away from the back of the eye. This leads to the appearance of floating spots in the individual’s field of vision, flashes of light and severe loss of vision. A detached retina represents a significant high risk of total vision loss if left unattended.
- Glaucoma: The normal flow of fluid in the eye becomes blocked as new blood vessels form. This blockage causes increase in occular pressure in the eye thus increasing the risk of optic nerve damage and vision loss.
Diagnosis:
Dilated eye examination:
The doctor puts the eye drops into the patient’s eyes. These drops help dilate the pupils of the eyes and allow the doctor to view the inside of the eye in a more detailed way.
Photographs are clicked of the interior of the eye. During the eye examination, the following abnormalities can be detected:
- abnormalities in the blood capillaries or vessels, optic nerve, or retina
- changes in eye pressure
- new blood vessels
- retinal detachment
- scar tissue
- Catract
Fluorescein angiography:
Sedating eye drops are used to dilate the pupils. A special dye-fluorescein is injected into a vein in the patient’s arm. Pictures are clicked as the dye circulates through the eyes. The dye may leak into the retina or stain the blood vessels if the blood vessels are abnormal.
This test helps to determine which blood vessels are blocked, leaking fluid. Any laser treatments can then be conducted. Approximately 24 hours after the test, the skin may turn yellowish and urine dark orange, as the dye exits the body.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
This scan provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina showing its thickness.
Treatment:
Injections:
Medicines called anti- VEGF drugs can slow down or reverse diabetic retinopathy. Other medicines like corticosteroids can also be used as a treatment.
Laser treatment or photocoagulation:
Laser helps in removing the scar tissue and cold compression in laser helps healing the leaked blood vessel
Vitrectomy :
This involves the removal some of the vitreous from within the eyeball. The surgeon replaces the hazy gel with a clear liquid.
Hope this article helps you understand the importance of eyesight and how to control diabetes to avoid DR.